Malaysia Sugar Industry Landscape
The players, capacity, and pricing mechanism of Malaysia's sugar industry
Bernas, the privately owned company that
monopolized rice importing is under the spotlight.
The sugar industry is also being controlled by the same owner. Let's understand the Malaysian sugar industry together.
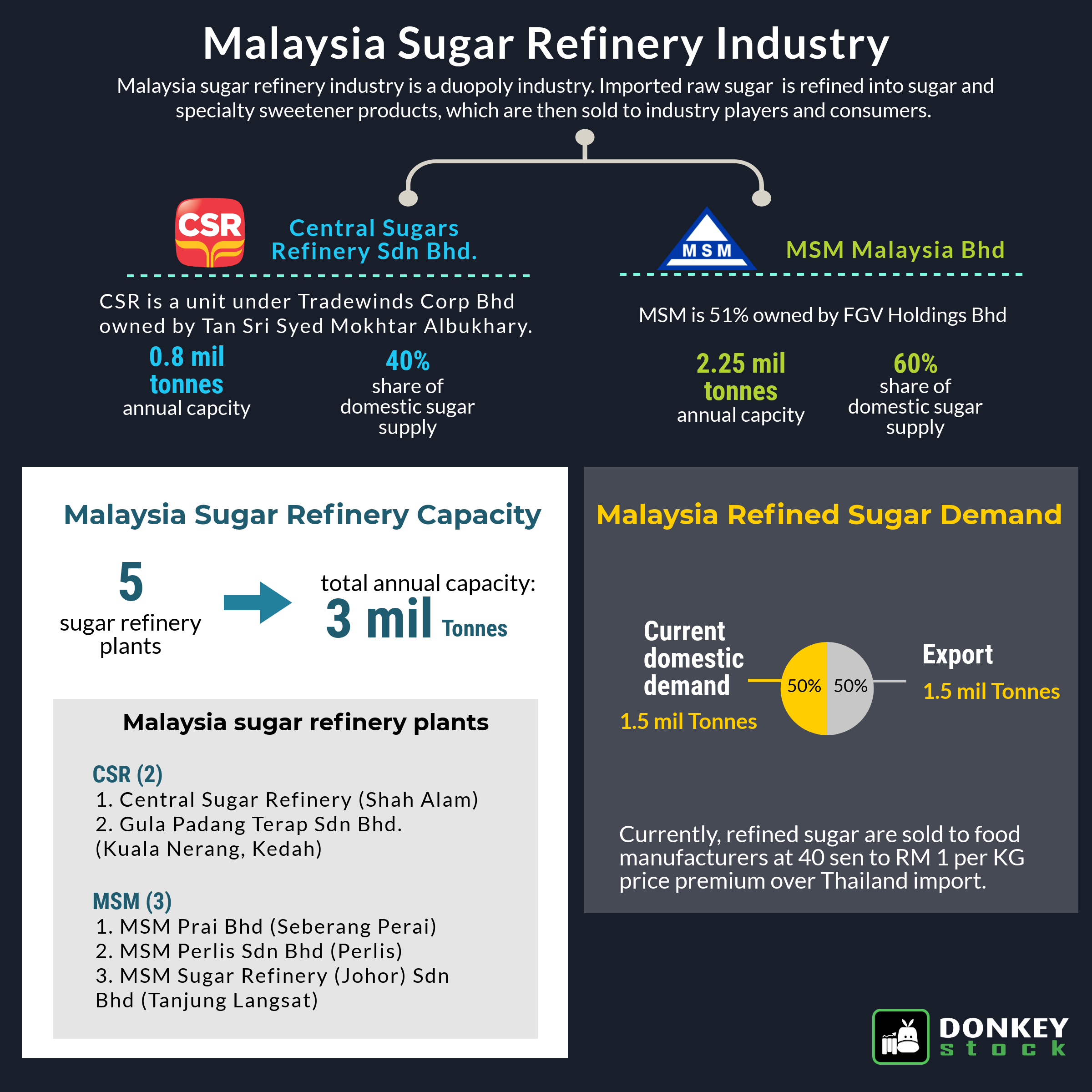
Sugar Landscape in Malaysia
In Malaysia, there are two sugar refiners –MSM
under FGV Holdings Berhad and CSR under Tradewinds (M) Berhad – operating five
sugar refinery. The 5 sugar refinery includes Central Sugar Refinery in Shah
Alam, Gula Padang Terap in Kuala Nerang, MSM Prai in Seberang Prai, MSM Perlis
in Chuping and MSM Sugar Refinery Johor in Tanjung Langsat.
The current total capacity of the five
refineries is 3.0 million metric tonnes per year. Domestic demand in Malaysia
is approximately 1.5 million metric tonnes per year, leaving Malaysia with an
excess capacity of 1,500,000 metric tonnes per year.
As part of the local refiners’ duty to ensure
sufficient sugar supply for Malaysia, a certain amount of sugar is stockpiled
to ensure adequate supply even during high world raw sugar prices.
Malaysia
Sugar Pricing
As sugar is gazetted under the Price Control
and Anti-Profiteering Act 2011 (Determination of Maximum Price – No. 2, Order
2017),
Currently, the domestic wholesale refined sugar price is
currently capped at RM2.69 per kilogramme (kg). The maximum price set by the
government for retail coarse sugar (Gula Pasir Kasar) is RM2.85 a kilogramme
and fine sugar (Gula Pasir Halus) is RM2.95 a kilogramme.
Reducing
Sugar Price Increases Risk
Sugar, must be used in moderation. As of 2013,
the Malaysian government removed the sugar subsidy in an effort to reduce the
rate of diabetes among Malaysians. Any further reduction to Malaysia’s already
cheap sugar might spur increased consumption.